Ceramic circuit boards are high-performance PCBs used for applications that require excellent heat dissipation, electrical insulation, high reliability, and environmental durability. Ceramic circuit board substrate materials include aluminum nitride (AlN), alumina (Al₂O₃), silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), and beryllium oxide (BeO). Based on the different manufacturing methods, ceramic circuit boards can be made by DPC, DBC, thick film, thin film, AMB, LTCC, or HTCC technologies.
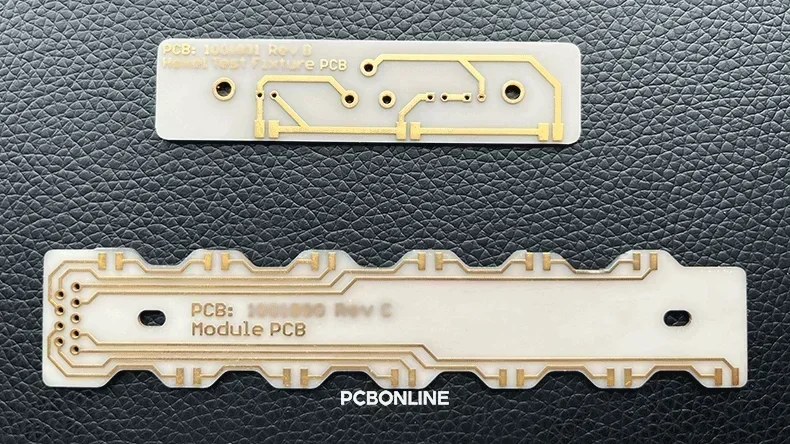

PCBONLINE, an advanced PCB manufacturer, provides one-stop ceramic PCBs available in various types to meet custom requirements. In this article, we provide an in-depth demonstration of ceramic circuit boards.
Pros and Cons of Ceramic Circuit Boards
Ceramic substrates provide superior thermal performance, excellent mechanical stability, and robust electrical insulation. Ceramic circuit boards are suitable for high-power modules, RF applications, automotive electronics, aerospace systems, industrial equipment, and medical devices.
Pros of ceramic circuit boards include:
- Superior thermal conductivity: Ceramic substrates provide thermal conductivity between 20 W/m·K and 270 W/m·K, significantly higher than FR4 (0.3 W/m·K) or standard metal-core PCBs. Ceramic circuit boards are ideal for high-power semiconductor packaging, laser drivers, IGBT modules, and LED lighting.
- Excellent electrical insulation: Ceramics act as strong electrical insulators while maintaining high thermal conductivity. Ceramic circuit boards can handle high voltages, making them suitable for power electronics.
- High-temperature resistance: Most ceramic materials can withstand continuous operation from -55°C to 250°C and short-term exposure to even higher temperatures without performance degradation. Ceramic circuit boards meet the requirements of automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
- Mechanical strength and chemical stability: Ceramic substrates resist corrosion, moisture, chemical attack, and mechanical wear. They also exhibit low thermal expansion, reducing the risk of cracking or delamination during thermal cycling.
- Long-term reliability: Due to their structural integrity and stable dielectric properties, ceramic circuit boards demonstrate high reliability in long-life, mission-critical electronic systems.
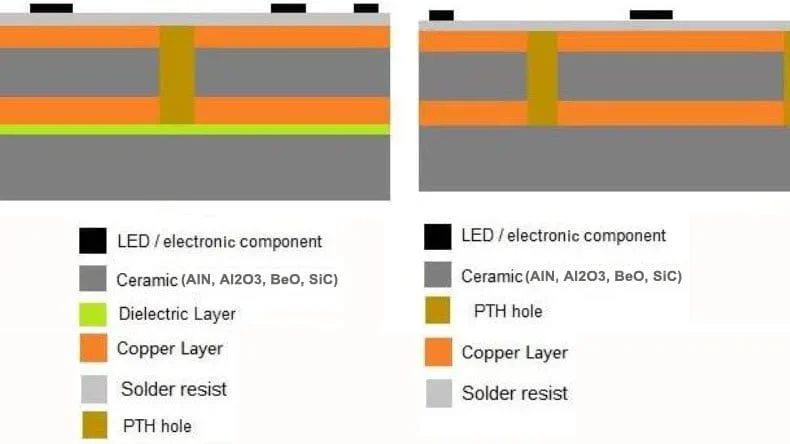
Despite their advantages, ceramic circuit boards also have cons:
- Higher cost: Ceramic substrates, especially aluminum nitride and silicon nitride, are more expensive to manufacture than FR4 or metal-core PCBs.
- Brittle nature: Ceramics can crack under excessive mechanical stress, requiring careful handling during assembly and installation.
- Limited PCB size: Ceramic substrates are generally produced in smaller panel sizes compared to FR4, limiting large-format PCB designs.
- Manufacturing complexity: Specialized processes and equipment are required for ceramic substrate metallization, which increases manufacturing lead time and cost.
- Despite these limitations, ceramic PCBs remain indispensable wherever performance and reliability take priority over cost.
Types of Ceramic Circuit Boards by Substrate Material
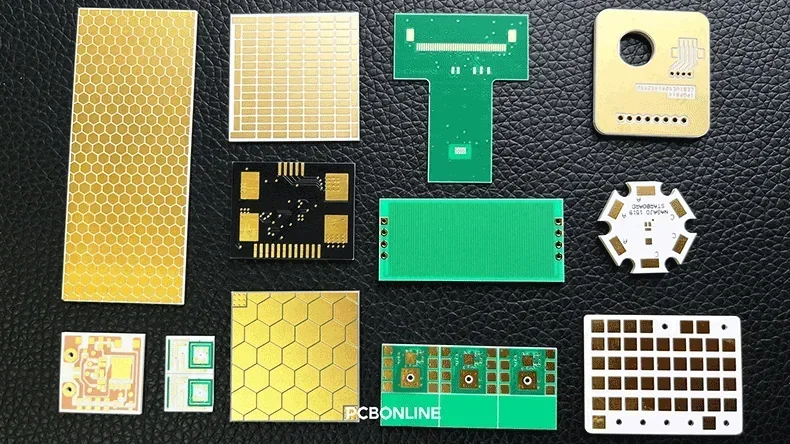
Ceramic PCBs can be categorized based on the type of ceramic substrate used. There are aluminum nitride, aluminum oxide, silicon nitride, and beryllium oxide ceramic circuit boards. Aluminum nitride and aluminum oxide are the two most common substrate materials used in ceramic circuit boards.
Aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramic circuit boards
Aluminum nitride is a ceramic material that offers excellent thermal conductivity, between 150W/m·K and 270W/m·K. AlN ceramic circuit boards are ideal for high-power applications that generate significant heat.
AlN ceramic circuit boards offer high thermal conductivity, good dielectric properties, low dielectric constant (~8.5), and good mechanical strength. Besides, they are compatible with DPC, DBC, and thin-film processes. They are the best ceramic circuit boards for applications where thermal performance is the highest priority.
The only drawback compared with alumina ceramic circuit boards is that AlN ceramic circuit boards are more expensive.
Aluminum nitride circuit boards are used in:
- Power semiconductor modules
- High-power LEDs
- RF systems
- Telecom base stations
- Laser diode packaging
Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic circuit boards
Alumina is also a commonly used ceramic substrate because it is cost-effective with balanced performance. Alumina ceramic circuit boards use 96% Al₂O₃, offering thermal conductivity around 20W/m·K to 30W/m·K.
Alumina ceramic circuit boards are the cheapest among all ceramic PCBs, and they offer moderate dielectric insulation, mechanical strength. Besides, alumina PCBs can be made by DPC, DBC, or thick-film technologies.
However, alumina ceramic circuit boards have a higher dielectric constant of about 9.5, so they are not suitable for high-power or high-frequency applications. They are used for:
- LED modules
- Mid-power drivers
- Sensor circuits
- Industrial electronics
Silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) ceramic circuit boards
Silicon nitride offers high fracture toughness and thermal conductivity of 70W/m·K to 90W/m·K, which is between alumina and AlN.
Si₃N₄ ceramic circuit boards have a high mechanical strength, low thermal expansion, and excellent thermal cycling reliability.
However, silicon nitride ceramic circuit boards are more expensive. Besides, their manufacturing is limited to the thin-film method.
Si₃N₄ ceramic circuit boards are used for:
- Automotive IGBT modules
- EV inverters and industrial converters
- High-reliability power control units
Beryllium oxide (BeO) ceramic circuit boards
Beryllium oxide offers extremely high thermal conductivity exceeding 250W/m·K. However, BeO is toxic, so the BeO ceramic PCB manufacturing is dangerous, and PCBONLINE does not provide BeO circuit boards.
BeO ceramic circuit boards are used in specialized aerospace and defense, and specialty high-power electronics.
Types of Ceramic Circuit Boards by Manufacturing Method
Ceramic circuit boards can also be categorized by the manufacturing method of applying conductive layers and creating circuit patterns. The ceramic circuit board manufacturing methods include DPC, DBC, thick-film, thin-film, AMB, LTCC, and HTCC.
DPC (direct plated copper) ceramic circuit boards
DPC uses laser activation and electroless copper plating followed by electrolytic copper thickening. DPC ceramic circuit boards support fine-pitch circuitry and thin copper layers.
DPC ceramic circuit boards have high precision, fine lines, smooth copper traces, and good adhesion. They are used for:
- RF modules
- High-frequency sensors
- Precision control electronics
- LED systems
DBC (direct bonded copper) ceramic circuit boards
DBC bonds copper foil directly to ceramic substrates through a high-temperature oxidation process. It supports thick copper up to 500µm and creates extremely strong copper–ceramic bonding.
DBC ceramic circuit boards have high current capacity and excellent thermal performance.
However, DBC ceramic circuit boards are not suitable for very fine-line circuits. They are used for:
- IGBT modules
- Power inverters
- Motor drives
- High-current LED boards
Thick-film ceramic circuit boards
Thick-film technology prints conductive, resistive, or dielectric pastes onto ceramic substrates using screen printing. The PCB pastes include silver, gold, or copper.
The thick-film process costs the lowest in ceramic PCB processes and is suitable for large-volume production.
However, thick-film circuits are not precise, the PCB surface is relatively rough, and the plated copper of the PCB has a lower conductivity. Thick-film ceramic circuit boards are used for:
- Heater circuits and LED boards
- Sensor modules
- Industrial electronics
Thin-film ceramic circuit boards
Thin-film circuits use vacuum deposition to apply ultra-thin metal layers onto ceramic substrates by sputtering or evaporation, followed by photolithography.
Thin-film ceramic circuit boards offer extremely fine lines and high precision, superior surface uniformity, and excellent RF and microwave performance. They are ideal for high-frequency and precision electronics.
However, thin-film ceramic circuit boards support a limited copper thickness and are suitable only for small circuits. They are used for:
- High-frequency RF modules
- Microwave components
- Aerospace electronics
- Miniaturized sensors
AMB (active metal brazed) ceramic circuit boards
AMB bonds thick copper directly to ceramic using active brazing alloys containing titanium. AMB ceramic circuit boards support very thick copper and are commonly used in electric vehicle applications.
AMB ceramic circuit boards have excellent thermal and mechanical reliability and strong metallurgical bonding.
However, AMB PCBs cost more than DPC and DBC PCBs, and their feature resolution is limited. They are used for:
- High-voltage power modules
- Automotive power electronics
- Industrial converters
LTCC (low-temperature co-fired ceramic) circuit boards
LTCC stacks multiple green ceramic tapes with internal conductive layers, which are co-fired below 1000°C. It allows multilayer ceramic boards with embedded components.
LTCC ceramic circuit boards support 10 to 60 layers, have excellent RF performance, and can embed passive components like inductors, capacitors, and filters.
However, LTCC ceramic circuit boards are expensive and are not suitable for high-power dissipation. They are used for:
- RF modules
- Antennas
- Filters
- Microwave systems
- Mobile and IoT devices
HTCC (high-temperature co-fired ceramic) ceramic circuit boards
HTCC uses alumina-based ceramic tapes co-fired at temperatures around 1600°C, with tungsten or molybdenum metallization.
LTCC ceramic circuit boards have strong mechanical strength and high reliability, and can withstand harsh environments.
However, LTCC ceramic circuit boards are expensive, and their RF performance is poorer than LTCC PCBs. They are used for:
- Aerospace electronics
- High-reliability industrial modules
- Hermetically sealed packages
PCBONLINE: High-Quality Ceramic PCB Board Manufacturer
PCBONLINE is a one-stop ceramic PCB board manufacturer founded in 2005, providing turnkey AlN PCB and alumina PCB made by any of the above manufacturing methods. Besides, ceramic IGBT modules, ceramic COB LED modules, ceramic LED plates, etc, can also be provided by PCBONLINE.

PCBONLINE manufactures, assembles, and tests ceramic PCBs as a source factory manufacturer under one roof, from prototypes to bulky production.
PCBONLINE can manufacture ceramic PCBs to be HDI, high-frequency, multilayer, and double-sided.
Provides one-on-one free and professional DFM (design for manufacturing) for ceramic PCB boards before and during prototyping/sampling to ensure the success of your project and seamless mass production.
PCBONLINE has powerful ceramic PCB manufacturing capabilities. The copper layer thickness of ceramic PCBs is arbitrarily customized from 1μm to 1mm.
High-quality ceramic PCB boards with no oxide layer on the PCB surface have better welding performance and high-temperature resistance.
For ceramic PCB manufacturing and assembly orders at $5,000 and above, we offer free complete ceramic PCBA samples and functional tests. If you are interested in ceramic PCB boards from PCBONLINE, feel free to send your inquiry to info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
Ceramic circuit boards use AlN, alumina, silicon nitride, or beryllium oxide as the substrate materials, and they can be made by DPC, DBC, thick-film, thin-film, AMB, HTCC, or LTCC. Selecting the substrate material and manufacturing methods based on the circuit layer, circuit precision, power, and RF requirements. To ensure the success of your PCB/PCBA projects, work with the turnkey ceramic PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE.
PCB assembly at PCBONLINE.pdf
PCB fabrication at PCBONLINE.pdf




