
In electronics manufacturing, while Surface Mount Technology (SMT) handles the miniature logic, THT remains the backbone of power electronics, heavy-duty connectors, and industrial control applications.
Founded in 2005, PCBONLINE has spent over two decades in printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) manufacturing. With two advanced PCB manufacturing bases and a turnkey PCB assembly factory, we have witnessed firsthand the transition from manual-heavy processes to high-precision automated systems.
Today, our facility is equipped with four automated SMT lines, four THT wave soldering lines, and a dedicated THT selective soldering line, allowing us to provide a comprehensive perspective on through-hole soldering.
Through-Hole Technology Used in 2026

Why are we still talking about through-hole soldering in 2026? The answer lies in mechanical integrity.
While SMT components are bonded to the surface of a PCB, THT components have leads that insert through the PCB holes, anchored by solder fillets on both the top and bottom layers.
THT soldering creates a joint that can withstand significant mechanical stress, thermal cycling, and vibration.
As electric vehicles, industrial robotics, and renewable energy storage systems become more prevalent, the demand for the robust "anchor" provided by through-hole soldering has seen a massive resurgence.
Currently, there are three through-hole soldering methods: hand soldering, wave soldering, and selective soldering.
|
Feature
|
Hand soldering
|
Wave soldering
|
Selective soldering
|
|
Production volume
|
Low (Hobbyist)
|
Very high
|
Medium
|
|
Precision
|
Variable
|
High
|
Ultra-high
|
|
Cost per joint
|
NA / (Labor)
|
Low
|
Medium/High
|
|
Thermal stress
|
Localized but long
|
Whole-board
|
Highly localized & short
|
|
Best for
|
Repairs
|
Standard THT PCBA
|
Complex, high-density PCBA
|

We are a B2B PCBA manufacturer, so we only accept PCB/PCBA orders from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), solution companies, and business makers, and provide SMT and through-hole soldering in wave soldering or selective soldering.
The PCBs we provide through-hole soldering or mixed technology (SMT + THT) usually contain these through-hole components:
- Connectors: Industrial cables are often heavy and frequently plugged/unplugged. THT pins provide the mechanical "leverage" to prevent the pads from ripping off the PCB.
- Electrolytic capacitors: These are often the "tallest" components. In an inverter, they handle significant ripple current. THT mounting keeps them stable against vibration.
- Heat sinks: These are heavy metal masses. THT mounting allows them to be bolted or soldered directly through the board for a rigid thermal path.
- Coils/inductors: Large copper windings in inverters carry high current. THT leads can handle the heat and the weight of the ferrite cores better than SMT pads.
- Power transistors (TO-220 / TO-247 packages): Inverters rely on MOSFETs or IGBTs. These are almost always THT because they need to be bolted to vertical heat sinks to dissipate the massive heat generated during power conversion.
- Fuses and varistors: Industrial controls need surge protection. Large MOVs and replaceable fuse holders are standard THT items for safety and easy maintenance.
- Transformers: For galvanic isolation in control circuits, THT pulse transformers are the gold standard for high-voltage clearance.
- Relays: Inverters and controllers often need to switch physical loads. The mechanical "click" and high current of a relay require the strong anchoring of through-hole pins.
PCBs that require through-hole soldering are used for:

- Programmable logic controllers: THT is used for the rugged I/O terminals and internal power isolation.
- Motor starters & contactors: High-current switching creates mechanical shock that only THT joints can withstand over thousands of cycles.
- Human-machine interfaces: While the screens are SMT-driven, the heavy-duty mounting brackets and power connectors are THT for physical stability.
- Variable frequency drives (VFDs): Used to control industrial motors; THT components handle the high-voltage "switching" stress.
- Solar & wind inverters: Large THT film capacitors and inductors are essential for filtering power before it enters the grid.
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS): Heavy-duty transformers and battery connectors rely on the deep anchoring of through-hole pins.
- Onboard chargers: Require THT for large magnetic components (transformers) that convert AC grid power to DC battery power.
- EV charging piles: DC fast chargers use massive THT busbars and connectors to manage currents that would melt standard surface-mount pads.
- Battery management systems (BMS): THT fuses and high-voltage isolation components ensure the battery pack remains safe under extreme conditions.
- Avionics control systems: THT joints are resistant to the "thermal fatigue" caused by the rapid temperature changes between ground level and high altitude.
- Ruggedized communications: Military-grade radios use THT for heavy shielding cans and RF connectors to ensure they survive impacts and drops.
- Grid-scale battery systems: These massive "power banks" use THT for their main power distribution boards, where the copper traces are often reinforced with THT busbars to carry hundreds of amps.
- Imaging systems (MRI/CT): The power supplies for these machines are enormous. THT is used for the power modules that drive the high-speed magnets and X-ray tubes.
- Surgical robots: While the "brains" are SMT, the "muscles" (the motors that move the robotic arms) use THT connectors and power drivers for maximum durability.
- 5G/6G base stations: Outdoor units are exposed to the elements 24/7. THT is used for high-power amplifiers and large heat-sink-mounted components to prevent failure from constant thermal expansion.

If your PCB is simple and hobbyist, you can turn to a B2C PCB manufacturer and manually solder the boards by your own, which is cost-effective.
Hand Soldering
Hand soldering is the most basic form of through-hole soldering, where a technician uses a soldering iron to apply heat and solder to individual joints.
Pros:
- Low setup cost: Requires no expensive machinery.
- Flexibility: Ideal for rapid prototyping or unique, one-off builds.
- Accessibility: Perfect for simple repairs or field modifications.
Cons:
- Inconsistency: Joint quality depends entirely on the technician's skill.
- Slow speed: Not viable for mass production.
- Thermal risk: Prolonged contact with a soldering iron can damage sensitive components or lift PCB pads.
For quality consistency, PCBONLINE never uses hand soldering for R&D prototyping. Only for specialized rework, our technicians may use a little hand soldering.
For both PCB prototypes and scalable production, we always use our automated lines to ensure 99.9% yield rate, quality consistency, and reliability.
Wave Soldering
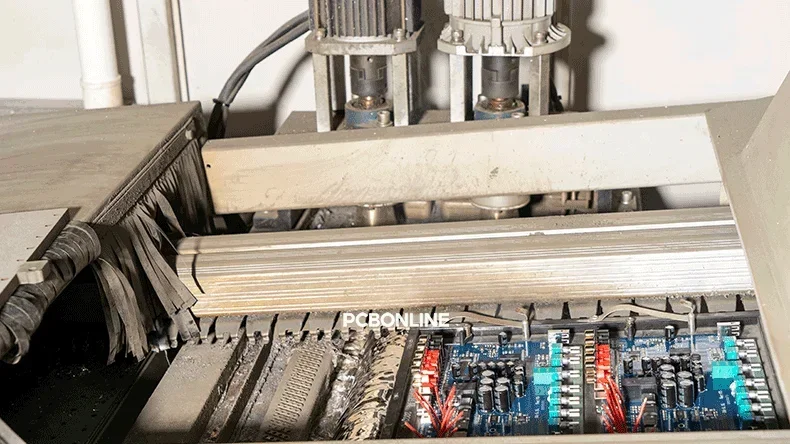
Wave soldering is a large-scale process where the entire underside of a PCB is passed over a wave of molten solder. At PCBONLINE, our four THT wave soldering lines are optimized for high-volume throughput.
How wave soldering works:
- Fluxing: A foam or spray flux is applied to clean the metal surfaces.
- Preheating: the PCB is heated to activate the flux and prevent thermal shock.
- Soldering: The PCB travels over a pumped wave of liquid solder, which wicks into the through-holes via capillary action.
The PCBONLINE Insight: Solving "Component Floatation"
One of the most persistent challenges in THT production, especially in mixed-technology PCBA boards, is component floatation.
Post-reflow, components may lift, leading to uneven surfaces and gaps.
At PCBONLINE, we solve this through two primary methods:
Custom fixtures: We design pallets that not only shield sensitive SMT parts from the heat but also apply downward pressure on THT components to keep them flush against the PCB.
Adhesive application: For high-precision items like buttons or sockets, we apply a specialized adhesive layer to the component base before it hits the wave, ensuring it stays perfectly aligned with the final product housing.
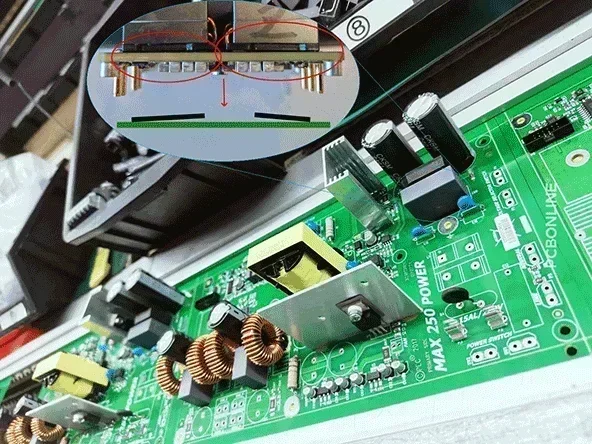
Selective Soldering
At PCBONLINE, our selective soldering line is reserved for complex PCBA boards where wave soldering is too "aggressive."
It uses a miniature fountain of solder (a nozzle) that moves along a programmed path to solder specific joints.
Why choose selective soldering for through-hole soldering?
![]()
- No fixtures required: Unlike wave soldering, which needs complex masks to protect SMT parts, selective soldering only touches the pins it’s told to touch.
- Reduced thermal stress: Only the specific joint is heated, protecting the rest of the PCB.
- Higher quality, higher cost: While it is slower than wave soldering, the defect rate is significantly lower for dense, double-sided PCBs.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) for Through-Hole Soldering
Successful through-hole soldering starts in the design phase. Based on our 20+ years of experience, here are the critical DFM factors for through-hole soldering for 2026.
- Hole-to-lead ratio
The clearance between the component lead and the plated through-hole (PTH) is vital. Too tight, and the solder won't flow; too loose, and the mechanical strength is compromised.
We typically recommend a hole diameter of 0.25mm to 0.40mm larger than the lead diameter.
- Thermal relief pads
When a through-hole is connected to a large copper plane (like a ground plane), it acts as a heat sink. This makes it difficult to reach the proper soldering temperature.
Tsolder> Tsub>liquidus+ 30°C
Using thermal relief pads ensures that the heat stays at the joint rather than dissipating into the PCB.
- Component orientation
For wave soldering, components should be oriented in a way that prevents "shadowing," where a tall component blocks the solder wave from reaching a smaller joint behind it.
At PCBONLINE, we don't just solder PCBs; we solve engineering challenges. Whether it's preventing component floatation with custom-designed fixtures or optimizing your BOM for selective soldering, our 20 years of expertise are at your disposal.
Part 6: One-Stop Through-Hole PCB Assembly Manufacturer
Due to the large area of through-hole soldering, the requirements for solder fullness, tin intake, and overall heat dissipation system are high.
In such a case, you'll need a professional PCB assembly manufacturer to provide through-hole PCB assembly.

PCBONLINE is a one-stop PCB assembly manufacturer with expertise, rich experience, and strong manufacturing capabilities for through-hole PCB assembly.
PCBONLINE pays attention to the details of through-hole PCB assembly, such as jig design, soldering oven temperature control, and production procedure design. This leads to PTH assembly success.
At PCBONLINE, wave soldering and selective soldering are both available for through-hole PCB assembly.
One-stop PCBA and ODM manufacturing because PCBONLIE is a source factory manufacturer providing R&D, PCB fabrication, component sourcing, PCB assembly, and box-build assembly.
Low-cost and high-quality PCB assembly and electronics manufacturing at PCBONLINE.
Offer a free PCBA sample and functional testing for bulk production.
PCBONLINE has many successful PCB assembly, ODM, and OEM manufacturing experiences, including high-power industrial converter boards, industrial HD cameras, electronic car chargers, EV charging piles, industrial controllers, and so on.
If you have any PCB assembly manufacturing needs, contact PCBONLINE at info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
The choice between hand, wave, and selective soldering is about which is right for your specific application. Choose wave soldering for cost-effective, high-speed production of standard designs. Choose selective soldering for high-reliability, high-density boards where precision is non-negotiable. Choose hand-soldering for your hobbyist board. To ensure the success of your through-hole or mixed-technology PCB project for industrial controls, automotive, motor drives, solar energy storage equipment, etc, get one-stop PCBA manufacturing services from the turnkey PCB assembly manufacturer PCBONLINE.




