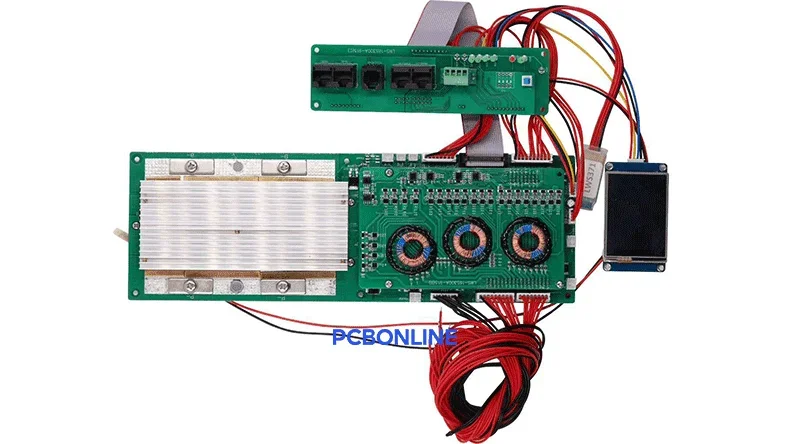
Figure: BMS control PCBA for mattery management system
A PCBA is a populated printed circuit board, where all required components are mounted together on a circuit board to create a functional system. Making PCBA is key to building reliable and effective electronic devices. PCBONLINE, a one-stop PCBA manufacturer, will walk you through everything you need to know about PCBA.
Part 1 . PCBA vs PCB
The terms PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) are often used interchangeably, but they represent two distinct stages in the electronics manufacturing process.
PCB (Printed Circuit Board): A PCB is a blank, bare printed wiring board. It's a rigid or flexible substrate with laminated and etched conductive pathways (copper traces), pads, and other features etched onto its surface. A bare PCB is the foundation; it cannot perform an electronic function on its own.
PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly): A PCBA is the result of the assembly process. It is a completed board where all the necessary electronic components have been mounted and soldered onto the PCB. It is a fully functional circuit ready for use in an electronic product. The components on the PCBA can be integrated circuits, resistors, capacitors, sensors, and connectors, among others.
Part 2. PCBA Classifications
The IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) sets standards for electronic manufacturing. While the IPC National Technology Roadmap for Electronic Interconnections is a broad guide, PCBA reliability and quality are typically classified under the IPC-A-610 standard, which defines three classes:
- Class 1 (General Electronic Products): This class is for products where the primary requirement is the function of the completed assembly. These are typically consumer electronics like remote controls and children's toys, where a limited lifespan and cosmetic imperfections are acceptable.
- Class 2 (Dedicated Service Electronic Products): This class is for products where continued performance and extended life are required, but uninterrupted service is not critical. These include devices like televisions and computers. Some visual imperfections are allowed, but the board's reliability must be higher than Class 1.
- Class 3 (High-Performance Electronic Products): This is the highest class, for products where continued high performance and on-demand operation are critical. Uninterrupted service is a must, and the device cannot tolerate downtime. Examples include military, medical, and aerospace applications. This class has the most stringent standards, and no cosmetic defects are allowed.
Based on the different assembly process requirements, the IPC National Technology Roadmap for Electronic Interconnections also published the following overall classification.
|
PCBA Class
|
Assembly Technologies/Requirements
|
|
Class A |
Through-hole (TH) components only
|
|
Class B |
Surface mount devices (SMD) only
|
|
Class C |
A mixture of Through-hole(TH) and simplistic SMD
|
|
Class X |
The complex intermix of through-hole (TH), simplistic SMD, fine pitch (FP), and ball grid array (BGA)
|
|
Class Y |
The complex intermix of Through-Hole (TH), simplistic SMD, Ultrafine pitch (UFP), and chip-scale package(CSP)
|
|
Class Z |
The complex intermix of Through-hole (TH), simplistic SMD, Ultrafine pitch (UFP), Chip On Board (COB), Flip Chip (FC), and Tape carrier package(TCP)
|
Part 3. What is Needed for Making PCBA
To create a PCBA, you need a combination of materials, equipment, and design files. If you lack any of them, no worries, the turnkey PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE will provide them to enable a smooth PCBA process.
- Design Files: To begin a PCBA process, you should provide the PCBA manufacturers, like PCBONLIN, with a Bill of Materials (BOM) listing all components, a Gerber file containing the blueprint for the bare PCB's copper traces, solder masks, and silkscreen, an NC-drilled file specifying the PCB hole positions, and your PCB requirements.
- Bare PCB: The unpopulated circuit board that serves as the foundation. If you have them manufactured, you can provide them to your PCBA manufacturer for PCB assembly. If you need PCB fabrication, the turnkey PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE can do it for you, ensuring the best quality.
- Electronic Components: The required parts on the PCBA, such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors, are listed in the BOM. The components for surface mounting (SMT) on the PCB are SMDs, and those for through-hole technology (PTH) assembly are PTH components.
- Solder Paste: A paste made of tiny metal alloys (usually tin, lead, and silver) that acts as a temporary adhesive and later forms the electrical connections. The PCBA manufacturers provide it, definitely.
- Assembly Equipment and materials: The PCBA manufacturers are equipped with machines and facilities to provide PCBA manufacturing. The equipment on a fully automated assembly line at PCBONLINE includes an automated loader, a solder paste printer, an SPI (Solder Paste Inspection) machine, three pick-and-place (PNP) machines for automated component placement (two high-speed PNP machines for mounting smaller-footprint SMDs, one functional PNP machine for mounting larger-footprint SMDs), a lead-free reflow soldering oven, and two AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) machines for quality checks before and after reflow. The machines on a half-automated PTH assembly line at PCBONLINE include a lead-free wave soldering oven and an AGV (automated guided vehicle) that transfers the wave soldering fixture between the workstations before and after wave soldering.

Part 4. Process of Manufacturing PCBA
The manufacturing process is a multi-step sequence, moving from a blank board to a finished, functional circuit. Based on the provided information, the process includes:
Solder Paste Printing and Inspection (SPI):
A stencil is used to apply solder paste precisely onto the component pads of the bare PCB. An SPI machine then inspects the thickness and placement of the paste to ensure it's correct.
Component Mounting:
Automated pick-and-place machines rapidly and accurately place both smaller Surface Mount Devices (SMD) and larger components onto the solder-pasted board.
Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI) Prior to Reflow:
A 3D AOI machine scans the solder paste and components to ensure no placement issues and the absence of poor soldering.
Reflow Soldering:
The populated board passes through a large oven with multiple temperature zones. The heat melts the solder paste, which then cools and solidifies to create permanent electrical and mechanical connections between the components and the board.
Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI) Following Reflow:
An AOI machine scans the PCBA board to check for defects like missing components, incorrect part polarity, or poor solder joints.
X-ray inspection:
PCBONLINE has two X-ray inspection machines for ensuring the hidden-joints SMDs' soldering quality. X-ray penetrates the PCBA without damage to check the solder balls and hidden soldering joints.
Through-Hole Technology (THT) Assembly:
Components with leads (pins) that pass through holes in the board are manually inserted. These are then soldered using a wave soldering machine, where the board is passed over a wave of molten solder.
First-Article Inspection (FAI):
After PCBA prototyping, PCBONLINE provides an FAI to ensure all the components on the PCBA sample are working well within the tolerance ranges. This prevents potential economic loss in mass production.
Functional Testing (FCT):
After PCB assembly, a functional test is performed to ensure the PCBA works as designed. This is often done using a custom jig to simulate the PCBA's operating environment.
Conformal Coating:
If you want PCBA coating, PCBONLINE can accurately spray a protective coating layer onto the circuit board and components.
IC programming:
If your PCBA has any IC and requires transferring your program into it, PCBONLINE can do it for you by local transferring into the IC or cloud transferring, depending on your preference.
Burn-in testing:
PCBONLINE can do the burn-in test to ensure your PCBA's long-term reliability after a long period of working. We can put the PCBAs into a temperature-programmed chamber and turn on the power to complete the burn-in test.
Enclosure and box-build assembly:
If you need box-build assembly for your PCBA project, PCBONLIE is happy to provide you with the custom-made enclosures and install them onto the PCBA to make them the finished devices.
You can watch the video about how PCBONLINE provides turnkey PCBA services.
Part 5. Components Needed for PCBA
A wide range of components can be mounted onto a PCBA, each serving a specific function. The most common components include:
- Resistors: Used to limit current flow in a circuit.
- Capacitors: Store and release electrical energy, smoothing the power supply, and filtering signals.
- Inductors: Store energy in a magnetic field, often used in filters and power supplies.
- Diodes: Allow current to flow in only one direction.
- Transistors: Act as electronic switches or amplifiers.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Also known as chips, these are complex circuits that integrate thousands or millions of components onto a single semiconductor die to perform specific functions.
- Sensors: Detect and respond to changes in the environment, such as temperature or light.

Part 6. DFM for PCBA Projects
DFM (Design for Manufacturability) is a design practice where engineers create a product with the manufacturing process in mind. For PCBAs, this involves:
Optimizing Trace Widths and Spacing:
Ensuring that the copper traces and the space between them are within the manufacturer's capabilities to prevent shorts.
Proper Component Placement:
Arranging components to allow for easy and efficient pick-and-place machine operation and to avoid overheating.
Accurate Footprints:
Using validated component footprints to ensure pads are the correct size and spacing for soldering.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer:
Collaborating with the PCBA manufacturer early in the design phase to align the design with their specific equipment and tolerances. This proactive approach helps reduce costs, improve quality, and accelerate time-to-market.

Is A PCBA An Electronic Module? It depends.
Yes, a PCBA can be considered an electronic module, but this depends on its purpose and complexity.
A PCBA is an electronic module designed to perform a specific, self-contained function and can be easily integrated as a sub-assembly into a larger device. For example, a Bluetooth module or a power management unit is are PCB that serves a modular function.
A PCBA can also be a finished product in itself if it is a simple device like a sensor or a single-board computer. When enclosed in a housing, it becomes a complete electronic device.
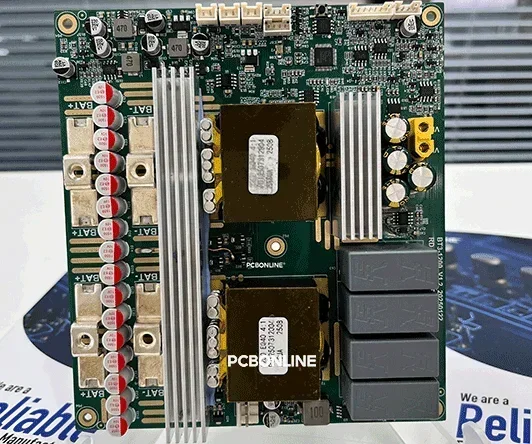

Figure: A high-power PCBA as the main board for industrial controls
On the other hand, some PCBAs are simply an electronic assembly. It is a sub-component that needs to be connected to other PCBAs or a main board to function. This is often seen in complex multi-board systems where different PCBAs handle separate parts of the overall functionality.
Partner with the one-stop PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE
PCBONLINE is a one-stop PCBA manufacturer that offers comprehensive electronic manufacturing services (EMS) from start to finish.

Our two advanced PCB manufacturing bases are in Jiangsu and Jiangxi Provinces, and our turnkey PCB assembly factory is in Shenzhen. Besides, we have an R&D team and a global supply network, with our component supply team centered in Hong Kong.
Our PCBA services include:
- PCB Fabrication: Manufacturing various types of bare PCBs, from prototypes to high-volume production.
- Component Sourcing: Procuring all necessary electronic components, saving the customer time and effort.
- Free DFM/DFT: We provide free Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Design for Testability (DFT) checks to ensure that designs are optimized for a smooth production process.
- PCBA Assembly: Providing both Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) assembly services in a single facility.
- Testing and Value-Added Services: Offering a range of quality assurance services, including X-ray inspection for hidden-joint PCBAs, first-article inspection, PCBA functional testing (FCT), IC programming, burn-in test, PCBA coating, enclosures, and box-build assembly.
We offer industrial-grade quality control – IPC-A-610 Class 2/3 certified assembly and strict inspection to ensure coating uniformity and defect-free protection.
Our one-on-one free and professional DFM before and during prototyping/sampling, helping you debug and improve design & component selection, to ensure the manufacturability, cost-effectiveness, and project success.
We offer cost-effective mass production with competitive pricing and fast lead times.
Our high-quality PCBA manufacturing is certified with ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, IATF 16949:2016, RoHS, REACH, UL, and IPC-A-610 Class 2/3.
PCBONLINE manufactures, assembles, and tests PCBs and PCBAs to box builds as a source factory manufacturer under one roof, from prototypes to bulky production, saving costs and time for you.
Whether you need consumer electronics PCBAs, industrial control PCBAs, medical-grade PCBAs, or military-grade PCBAs, PCBONLINE can handle the full PCBA process in-house. To get a quote for your PCBA project, email us at info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
A PCBA is the key to building electronic devices. By partnering with an experienced turnkey PCBA manufacturer like PCBONLINE, you get not only the right PCBA supply but also R&D support and quality assurance.
PCB assembly at PCBONLINE.pdf




