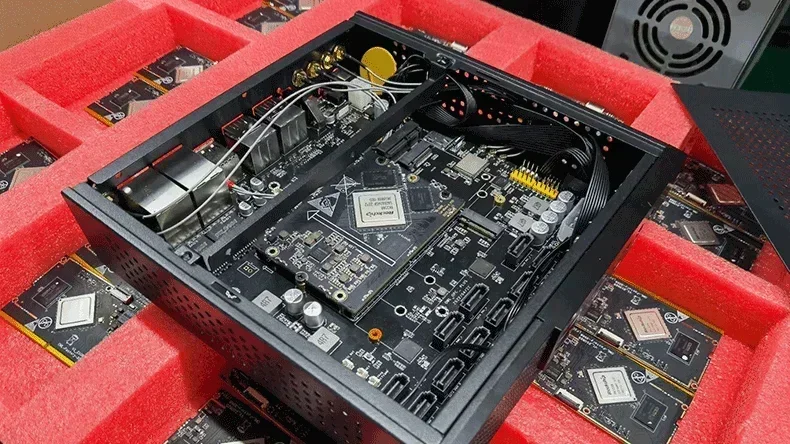

In electronics, the two terms "motherboard" and "circuit board" may be used interchangeably, creating confusion. However, a motherboard and a circuit board are not quite the same thing. A system or equipment can have various circuit boards, and a motherboard is the main circuit board playing the core functions.
In this article, we will understand what motherboards and circuit boards are, how they differ from each other, and what their roles are.
In this article:
Part 1: What is a Circuit Board? Part 2: What is a Motherboard? Part 3: Difference between Motherboard and Circuit board Part 4: Frequently Asked Questions about Motherboards and Circuit Boards One-Stop PCBA Manufacturer for Motherboards and Advanced Circuit BoardsWhat is a Circuit Board?
A circuit board is a PCB (printed circuit board), which is the backbone of modern electronics. It is a flat platform that connects different components like resistors and capacitors and allows them to work together. Without it, putting together modern electronics would be much harder.

Types of Circuit Boards
There are different kinds of circuit boards, and they are made for various purposes, such as:
- Single-layer circuit boards: They are the simplest circuit boards with components on one side. Single-layer FR4 PCBs are the most common circuit boards. Aluminum PCBs, flexible PCBs, copper-core PCBs, and ceramic PCBs are usually single-layer.
- Double-layer circuit boards: These have two copper circuit layers, and their component can be on one side or both sides. Double layers are common for FR4 PCBs and flexible PCBs.
- Multi-layer circuit boards: They have up to 64 circuit layers for more advanced designs and are found in middle and high-end applications such as smartphones and computers.
- Rigid circuit boards: These are solid boards that do not bend. FR4, copper, PTFE, and ceramic PCBs are rigid circuit boards. Aluminum circuit boards are usually rigid.
- Flexible circuit boards: Flex PCBs are those that can bend and twist. PI (polyimide) and PET (polyester) circuit boards are flexible. They are used in LED lights, screen displays, wearable devices, etc. Flexible aluminum PCBs also exist.
- Rigid-flex circuit boards: They essentially belong to flexible PCBs as their inner layers are PI flexible PCBs. Their outer layers are FR4. Computers, laptops, and medical equipment use rigid-flex circuit boards.
- Ceramic circuit boards: They are made from ceramics, including alumina and aluminum nitride. Thanks to their small DK/Df values, good thermal dissipation, and high-temperature resistance, ceramic PCBs are used for high-frequency or high-temperature applications like automotive sensors, solar energy storage modules, and high-power LED lights.
What Circuit Boards Do
Circuit boards are not just for holding components. They have several important functions, such as:
- Support: They hold components in place.
- Electrical connections: Copper traces connect everything, which creates a working circuit.
- Signal transmission: They let power and data flow between components smoothly, which allows the components to communicate.
- Thermal dissipation: The metal-core and ceramic circuit boards can dissipate heat quickly to protect the device from overheating.
A circuit board doesn't mean it's a motherboard. A motherboard is a different kind of board, which is discussed in the next section.
What is a Motherboard?
A motherboard is a type of circuit board, but it is much more specific. It is the central hub of a system, connecting all major components and ensuring their work together. Motherboards are designed to handle more complex tasks and support the addition of more hardware.

Features of a motherboard
- Centralized control: It links up the processor, memory, and storage devices.
- Expandability: Motherboards have slots for upgrades like adding more RAM or a better graphics card.
- Multi-layer construction: They have several layers to support high-speed communication.
- Power distribution: It sends power to the other components.
- Data communication: The motherboard manages data transfer between different parts of the system.
Examples of motherboards in devices
- Computer motherboard: This connects all the essential parts in a computer such as CPU, RAM, storage, and graphics card. It also provides ports for things like USB and audio.
- Smartphone mainboard: This holds the processor, memory, and wireless components. Smaller boards connect things like the camera.
- Industrial control motherboard: It controls automation in factories, connecting to sensors and controllers.
Difference between Motherboards and Circuit boards
While a motherboard is a circuit board, it has some key differences that set it apart from a normal circuit board, such as,
- Purpose: A circuit board is usually designed to handle one task, like regulating power. A motherboard is like a manager that integrates everything and ensures that the system works.
- Complexity: Circuit boards can be simple or complex. Motherboards are almost always more complex and consist of multiple layers and connections.
- Connectivity: A motherboard is the main point of connection for all components. Other circuit boards typically work on their own or in smaller systems.
- Expandability: Most the circuit boards have a fixed function, but motherboards allow you to upgrade and add new components.
Take a computer as an example to tell the difference between a motherboard and a circuit board. The computer motherboard connects the CPU, memory, and storage, while smaller circuit boards handle specific tasks like video output or Wi-Fi.
A smartphone works similarly: the mainboard integrates everything, while smaller circuit boards control individual features.
Computer motherboard and circuit boards
Frequently Asked Questions about Motherboards and Circuit Boards
1. Is the largest circuit board always the motherboard?Not always. The largest board could be a backplane or a baseboard, not the motherboard. The motherboard connects the key components.
2. Can a device have more than one motherboard?Most devices have one motherboard, but bigger and complex systems such as servers sometimes have multiple boards that connect, known as daughterboards or expansion boards.
3. What happens if the motherboard breaks?If the motherboard fails, the whole system usually stops working. A failure in a smaller circuit board, though, might just affect a particular function like Wi-Fi or sound while the rest of the device still works.
4. Are all motherboards PCBs?Yes, every motherboard is a PCB. It is just a more advanced PCB that connects and integrates the main components.
5. What materials are circuit boards made from?Circuit boards and motherboards are usually made from fiberglass, copper, and sometimes gold. Higher-end motherboards might use gold for better conductivity.
One-Stop PCBA Manufacturer for Motherboards and Advanced Circuit Boards
If you want to build a system or equipment with a motherboard and the rest of the circuit boards, you can work with the one-stop PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE from prototypes to bulky PCBA production and box-builds.
Founded in 1999, PCBONLINE has two large advanced circuit board manufacturing bases, one EMS PCB assembly factory, an R&D team, and stable supply chains. Besides, it has long-term cooperation with the top 3 mold manufacturers in China to manufacture the enclosures for box build assembly and SMT stencils, jigs, and molds for PCB assembly. What's more, it has strategic cooperation with the MCU manufacturers like Espressif, Neoway, Quectel, etc.

PCBONLINE provides free and professional DFM (design for manufacturing) for motherboards, circuitboards, and box-build projects before and during prototyping/sampling to ensure the success of your project and seamless mass production.
Strong manufacturing capabilities to meet your custom requirements for motherboards, PCBAs, and assemble the final boards with enclosures.
One-stop circuit board manufacturing with comprehensive testing and value-added services, including R&D, prototyping/sampling, PCB fabrication, component sourcing, PCB assembly, conformal coating, IC burn-in, enclosures, and box-build assembly for the final devices.
High-quality circuit boards and motherboard manufacturing certified with ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, IATF 16969, RoHS, REACH, UL, and IPC-A-600 Class 2/3.
No MOQ for circuit baords. Free prototyping/sampling, R&D, PCBA functional testing, and IC burn-in for mass production orders.
With PCBONLINE as your motherboard and PCBA manufacturer, you can ensure the success of your project and save big in costs and time. For inquiries and quotes, contact PCBONLINE's team at info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
All motherboards are circuit boards, but not all circuit boards are motherboards. A circuit board connects components for a specific task, while a motherboard acts as the central hub of a system, linking everything together and doing the heavy lifting. Furthermore, a motherboard provides options from extensions and is complex.
Once you understand their difference, it is easier to see how devices like computers and smartphones are built and are being operated. If you want to talk with experts about your motherboard or equipment project, contact PCBONLINE by email or chat with us from the online-chat window.PCB fabrication at PCBONLINE.pdf




