
Mass production of modern consumer and industrial electronic devices relies heavily on Surface Mount Technology (SMT). SMT enables the speedy and reliable PCB assembly of high-performance, high-density circuit boards. SMT-based PCB manufacturing involves several critical process stages, including soldering, during which components are attached to the surface of the circuit board. Reflow soldering is one of the most widely used techniques in PCB manufacturing due to its ability to produce consistent and high-quality joints.
Precise temperature control is a key requirement in the reflow soldering process, as even slight deviations in temperature can lead to defective joints or thermal damage. This level of control is achieved through the use of a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller.
PID controllers are widely used in industrial applications for their ability to provide accurate control with fast response times and minimal error.
Beyond temperature regulation, PID controllers are also commonly used for position, flow rate, level, and pressure control.
Basics of Reflow Soldering Process
Reflow soldering ovens automatically solder SMT electronic components on the PCB. These machines consist of distinct temperature zones: pre-heating, soaking, reflow, and cooling. Therefore, accurate temperature control is crucial for maintaining the correct temperature profile throughout the reflow soldering process.

In the pre-heating zone, the temperature increases gradually to avoid thermal shock to the PCB and components.
In the soaking zone, a uniform temperature is maintained to minimize the risk of thermal stress. The actual soldering of components to the PCB takes place in the reflow zone, where the solder paste melts and joints are formed.
In the cooling zone, rapid cooling is achieved to prevent grainy solder joints and contact bridging.
Thus, it is clear that precise temperature control is a key requirement for reflow soldering ovens. Improper temperature regulation can lead to issues such as cold joints, overheating (damaging the PCB or components), and tombstoning (lifting of components from one end). To eliminate these problems, PID controllers are employed for accurate temperature control in reflow soldering ovens.
Basics of PID Control
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control is a widely used closed-loop control strategy employed for the precise regulation of analog process variables such as temperature, pressure, level, position, and mass flow rate. The PID controller continuously calculates the difference between the setpoint and the actual process variable, and adjusts the output accordingly to minimize the error as much as possible.
The PID controller consists of three functional blocks—Proportional, Integral, and Derivative.
The Proportional block produces an output proportional to the error, providing a real-time corrective response. The Integral block deals with the accumulation of past errors and eliminates steady-state error by adjusting the output. The Derivative term predicts future errors by measuring the rate of change, helping to dampen the system response and reduce overshoot. Together, these three blocks ensure accurate, precise, and stable control of process variables.
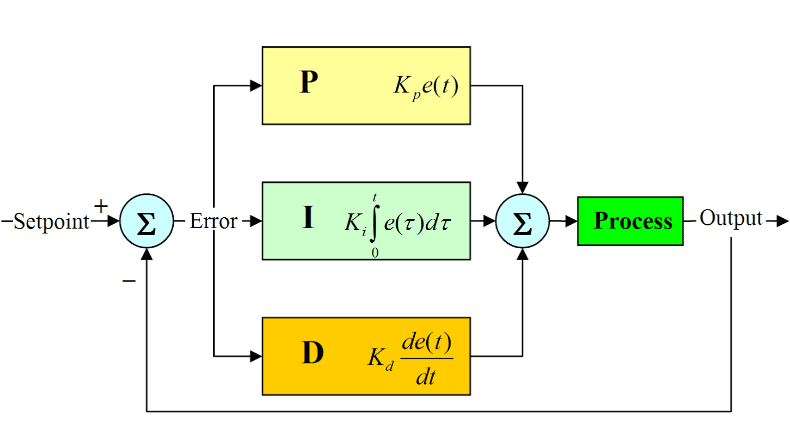
PID controllers are ideal for controlling analog process variables due to their ability to manage gradual changes and maintain stable process conditions. In reflow soldering ovens, PID controllers gradually adjust the temperature to reach the desired setpoint. This minimizes temperature oscillations and enables smooth, proportional control of the heating elements.
One drawback of PID controllers is the difficulty of tuning, which often involves a trial-and-error approach. Improper tuning can lead to issues such as thermal inertia, overshoot, oscillations, and accumulated errors. Nevertheless, PID controllers remain widely used in industrial control systems due to their high accuracy, stability, and robustness.
PID Controller Design for Reflow Soldering System
The PID control strategy for reflow soldering ovens can be implemented either through analog op-amp-based circuits or using digital microcontrollers. Most modern PID control systems are built around microcontroller-based embedded platforms, where the PID algorithm runs on the microcontroller. Commonly used microcontrollers for industrial-grade applications include STM32, MIPS, ESP32, and AVR families.
Reflow soldering ovens are equipped with K-type thermocouples for temperature sensing. The raw sensor signal is amplified using dedicated ICs such as the MAX6675 or MAX31855. These ICs act as an interface between the analog thermocouple and the digital microcontroller. The microcontroller running the PID algorithm implements a closed-loop control system using feedback from the temperature sensors and actuates the heating elements accordingly.
The heating elements of reflow soldering ovens are controlled through Solid State Relays (SSRs) or TRIACs. The current supplied to the heating elements is regulated by the PID algorithm based on real-time thermocouple feedback.
The cooling fans in reflow systems are typically driven by microcontroller-generated PWM signals, enabling variable speed control for efficient cooling. The user interface is typically implemented using TFT or LCD displays, accompanied by pushbuttons or selector switches, allowing operators to configure and monitor various machine parameters.
Thermal cutoffs, fuses, and watchdog timers are commonly integrated into the circuit for protection against overcurrent, overheating, electrical faults, and firmware-related issues, ensuring safe and reliable system operation.

Components of the Reflow Soldering Oven
The overall circuit of the reflow soldering oven consists of a low-voltage control system and a high-voltage actuator system.
The low-voltage section includes the microcontroller, ICs, and other sensitive electronic components. The high-voltage section comprises SSRs, TRIACs, or power MOSFETs, along with relays, fuses, MOVs, contactors, and other high-power circuit elements.
Isolation between the low-voltage (LV) and high-voltage (HV) sides of the circuit is typically achieved using opto-isolators, ensuring safety and signal integrity. For thermal management, heat sinks and cooling fans are integrated into the PCB to dissipate heat from power components.
Additionally, decoupling capacitors and filter circuits are used to suppress electrical noise and electromagnetic interference, enhancing system reliability and signal integrity.
PID System Design Challenges and Solutions
There are several technical challenges associated with the design of PID controllers for reflow soldering ovens. The first major issue is thermal lag and temperature overshoot caused by inaccurate PID tuning, which can lead to cold solder joints and component damage. This problem can be mitigated by accurately tuning the PID controller.
The second major issue is the corruption of sensor data due to noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI). This issue can be addressed by incorporating filter circuits.
Another significant challenge is the flickering of power switching devices such as SSRs or TRIACs. This issue can be resolved by selecting an appropriate switching frequency for the power switching components.
Last but not least, PCB warping caused by uneven heating is a critical concern. This is handled by implementing a multi-zone heating system in reflow soldering ovens, which ensures uniform airflow inside the oven and maintains a consistent temperature profile across the entire PCB.

Partner with PCBONLINE for SMT PCB Assembly
SMT PCB assembly is the backbone of the modern electronics industry. If your project requires both SMT and PTH assembly for electronics manufacturing, partner with PCBONLINE, an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) that delivers complete, turnkey solutions.

PCBONLINE is an OEM PCBA manufacturer founded in 1999. It has two large advanced PCB manufacturing bases independently fabricating all types of PCBs, one EMS (electronic manufacturing service) PCB assembly factory with two component warehouses, stable supply chains, and an R&D team. Besides, it keeps long-term cooperation with the top 3 mold/enclosure manufacturers in China to provide the molds, jigs, and enclosures for full box-build solutions.
Each SMT line at PCBONLINE is equipped with complete machines, including three advanced pick-and-place machines, dual AOI machines, and a lead-free reflow soldering oven.
The CAM engineers at PCBONLINE have rich experience in reflow profiles and temperature control.
Our SPI and dual AOI systems perform 3D surface scanning, offering thorough and accurate inspections for superior quality control throughout the process.
We conduct first-article inspections both before prototype assembly and before mass production to ensure the highest PCBA quality and prevent costly issues.
Our experienced R&D and engineering teams provide one-on-one support, solving technical and non-technical challenges while offering optimization suggestions to ensure your project runs smoothly from start to finish.
High-quality PCBA manufacturing certified with ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, IATF 16949:2016, RoHS, REACH, UL, and IPC-A-610 Class 2/3.
When your project enters the bulky production stage, PCBONLINE refunds the fees of prototyping, including its value-added services.
Reflow soldering ovens play a pivotal role in the production of SMT circuit boards, and at PCBONLINE, the reflow ovens are advanced. No matter what quantity of boards you order, PCBONLINE prioritizes quality. To get a quote from the SMT PCBA manufacturer PCBONLINE, contact info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
In modern digital systems, PID controllers are typically implemented as algorithms running on a microcontroller. The microcontroller, together with the PID algorithm, thermocouples, and actuators, forms a closed-loop feedback control system for precise control of the heating elements. Proper tuning of the PID controller is essential to ensure stable and smooth operation of the reflow soldering oven. To ensure the success of your PCB/PCBA projects, work with the turnkey advanced PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE.
PCB assembly at PCBONLINE.pdf




