
flexible medical PCB for gastroscopy manufactured by PCBONLINE
In this age of rapid technological development, the healthcare industry is also going through innovations. At the heart of this revolution is Medical Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) that power modern medical devices. Medical PCBs are accurately designed boards to operate under the dynamics of a health care system.
In this article, we will discuss the types and assembly of medical PCBs, their challenges, and industry standards.
In this article:
Part 1. Types of Medical PCBs Part 2. Compliance Requirements for Medical PCBs Part 3. Medical PCB Assembly Part 4. Challenges and Trends for Medical PCBs Part 5. One-stop Medical PCB and Assembly ManufacturerTypes of Medical PCBs
A medical Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is designed and manufactured to ensure that it serves the rigorous demands of the healthcare system. They are indispensable in medicine and healthcare as research, therapeutic, and diagnostic techniques require automation. From life-saving pacemakers to advanced imaging systems like MRI and CT scanners, medical PCBs form the backbone of the technology that defines contemporary medicine.
The medical PCB industry is evolving with HDI technology to enable smaller, denser boards with high-speed connectivity. This requires rigid, flexible, and rigid-flex constructions for three-dimensional configurations. The following are several types of PCBs that the medical industry uses today.
HDI PCBs
High-density-interconnect (HDI) PCBs's advanced construction allows for packing many miniature components and interconnections into a small form factor. HDI PCBs help to create compact medical devices maintaining high performance. Health technology devices such as sensors and wearable devices typically use HDI PCBs.
Rigid PCBs
The Rigid PCB is made from solid and inflexible materials and maintains its shape and structural integrity over time. These are used in most stand-alone and some portable medical equipment as their performance benefits from these rigid PCBs in demanding applications. The following image shows a rigid PCB.

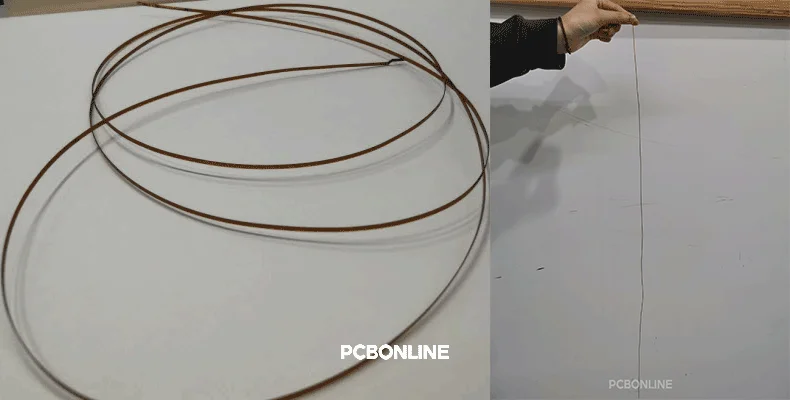
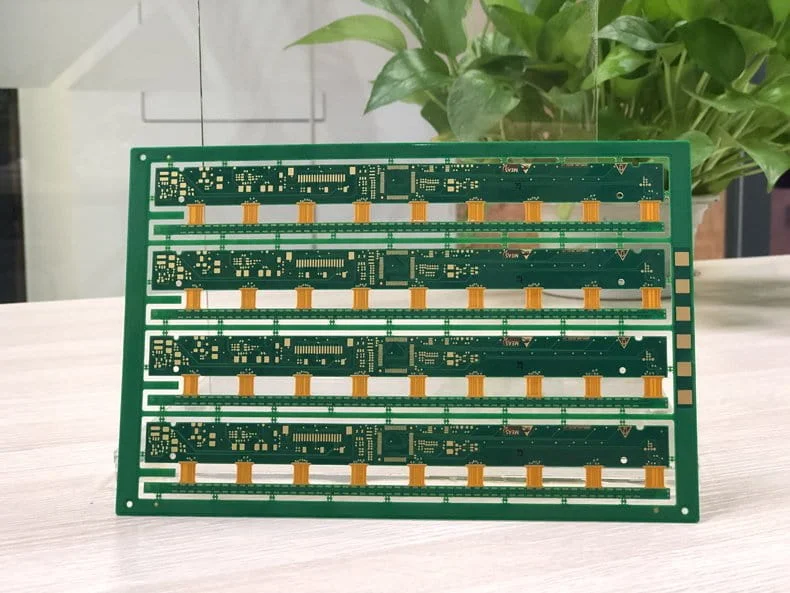
Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs are made of material that allows the PCB to bend and fold. This flexibility enables patients to wear the medical devices on their bodies. The next image demonstrates a flexible PCB manufactured by PCBONLINE for medical testing.

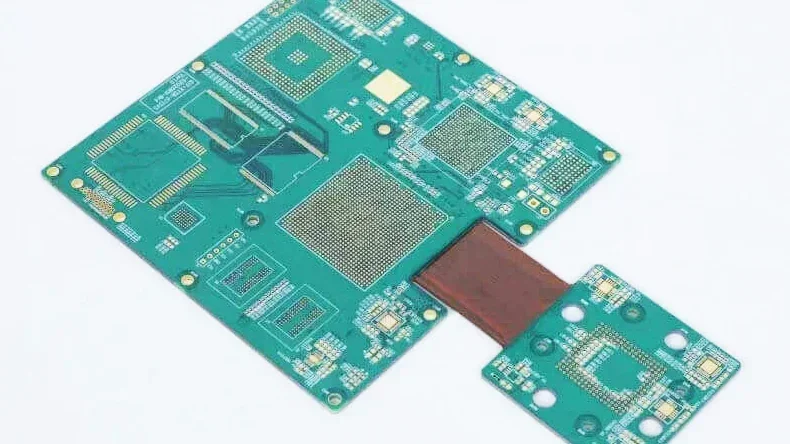
Rigid-flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs include the internal flexible PCB layers and the external FR4 PCB layers. The unwanted FR4 areas are removed by laser to expose the flexible part. This arrangement helps to make more compact medical devices without compromising their performance. Portable diagnostic equipment and implantable medical devices use rigid-flex PCBs as shown in the following picture.
Within the above broad categories, the medical PCBs are designed according to the following classification depending upon the specific usage.
According to the different layers, the medical PCBs can be classified as:
Single-layer PCBs
These PCBs as their name suggests consist of a single layer of conductive material on a substrate. Their cost-effectiveness makes them suitable for simple and basic medical devices. These are utilized in devices such as simple sensors and temperature monitors. For instance, the next image shows a heart-rate sensor containing a single-layer PCB.
Double-layer PCBs
These boards consist of two conductive layers on both sides of a substrate. The two layers provide greater routing options, which allow for moderate complexity. Double-layer PCBs are commonly found in medical devices such as infusion pumps and ECG machines. The following image shows an infusion pump PCB.
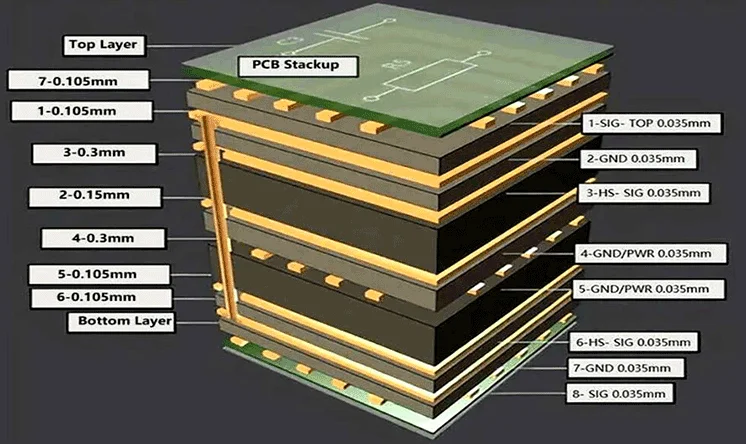
Multi-layer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs consist of alternate layers of substrates and conductive materials. Multiple conductive layers offer still higher routing density. Therefore, these boards are suitable for complex medical devices. Within a small form factor, they can hold many miniature components. This allows the PCB advanced functionalities. Multi-layer PCBs are common in many high-end diagnostic equipment, and medical devices like CT scanners, and MRI machines. The next image shows an illustration of a stacked, multilayer PCB.
Compliance Requirements for Medical PCBs
Several global and national organizations monitor medical PCBs. They help in PCB standardization. This ensures PCBs meet the requirements of safety.
IPC RegulationsIPC stands for Industry for Printed Circuits. The IPC regulates the assembly of a wide range of electronic equipment including medical PCBs. These standards include:
- IPC-A-600, outlining conditions for acceptable circuit boards
- IPC-A-610, outlining the acceptability of electronic assemblies
- IPC-A-6012, outlining the performance and qualifications of rigid PCBs
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) regulates the design and manufacturing of PCBs. They offer guidelines for a detailed quality management system. The required standards for medical PCBs are:
- ISO 9001:2015, for quality requirements during PCB design, manufacturing, and assembly
- ISO 13485:2016, for an updated QMS for PCB manufacturers
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the USA regulates medical devices. This includes those with PCB assemblies. The manufacturers have to conform to the comprehensive requirements for documentation, design control, and validation.
RoHS ComplianceThe RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Materials) directives restrict the usage of specific hazardous materials during the manufacturing and assembly of PCBs for the medical industry.
IEC60601 CertificationIEC stands for International Electrotechnical Commission. The IEC 60601 certification is a series of international standards that ensure the safety and performance of medical electrical equipment. This certification signifies that the PCB manufacturing processes meet rigorous performance standards, and the PCB assembly techniques meet necessary safety standards.
Medical PCB Assembly
Besides PCBs, the one-stop PCBA manufacturer provides medical PCB assembly with value-added services custom meeting all your project's demands. All medical PCB assembly has to be lead-free.
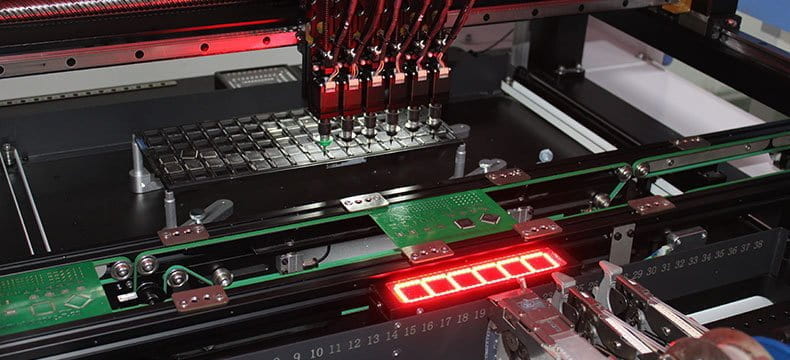
Medical PCBs include SMT (surface-mount) and THT (through-hole) assembly. The PCBA value-added services include functional testing, conformal coating, IC programming, thermal aging, enclosures, box-build assembly, and application simulation testing.
The lead-free SMT assembly process is fully automatic. It includes solder mask printing > solder paste inspection > picking and placing components> reflow soldering > automated optical inspection (AOI). If the PCBA has a BGA or other components that require internal inspection, there's the X-ray inspection before reflow soldering. If the medical PCB for assembly is double-sided, the PCBA goes through the SMT line twice. If the PCBA is possible to oxidize, the reflow soldering can shift to nitrogen reflow.
The lead-free THT assembly process is half-automatic and is only required when the medical PCB has through holes. It includes inserting the leads through the PTH holes > wave soldering. If the PCBA is thermally sensitive, the wave soldering process can shift to selective soldering.
Challenges and Trends for Medical PCBs
The medical industry is highly regulated and needs to follow certain standards to ensure that the manufactured equipment is of the highest quality. The safety of patients is an important factor in this application and tremendous pressure for safety, consistency, and reliability is required from the PCB. This presents a variety of challenges, particularly when it comes to PCB manufacturers. To meet these regulations and demands, manufacturers must consider factors such as method validation, facility approval, part limitations, and high production costs.
Method validation:The process used to manufacture medical PCBs must be validated for accuracy and safety. This includes validating the environmental conditions of the manufacturing environment, and ensuring proper parameters are met during each step of the production process.
Facility approval:Manufacturers of medical PCBs also need the approval of the relevant authorities before they can produce any product for sale. This means that they have properly maintained and calibrated equipment as well as an effective quality check in place.
Part limitations:Medical PCBs have an inherent limitation due to their size and complexity. For example, parts may need to be extremely small or densely packed together, which can create difficulties in terms of reliability and fabrication. Additionally, certain materials used such as copper and silver may not be suitable for use in some applications due to their reactivity with other materials. On top of all, PCB designers must also consider the impact of electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the performance of their products.
Trends in Medical PCBs
As the demand for smaller and less invasive medical devices surges, so does the need for specialized PCBs. The medical PCB industry uses HDI technology to allow the smaller but denser boards to signal high-speed connectivity. To satisfy increasingly strict design criteria, many manufacturers are now utilizing non-traditional form factors. This may require flex or rigid-flex constructions that enable three-dimensional configuration choices. Combined with these advanced technologies are demands for features like high-speed signal transmission. Such solutions can guarantee reliable performance even in the most arduous of conditions.
One-stop Medical PCB and Assembly Manufacturer PCBONLINE
If you need medical PCBs and PCB assembly to meet your project's demands, you can work with the one-stop medical PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE.

Founded in 1999, PCBONLINE has two large advanced PCB manufacturing bases, one PCB assembly factory, stable supply chains, and an R&D team.
PCBONLINE provides turnkey medical PCB manufacturing, including R&D, prototyping, PCB fabrication, component sourcing, PCB assembly, PCBA value-added, and box-build assembly.
PCBONLINE offers free DFM (design for manufacturing) and one-on-one engineering support throughout your medical PCB project to ensure a smooth manufacturing process and successful results.
High-quality medical PCB and PCBA manufacturing certified with ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, IATF 16949:2016, RoHS, REACH, UL, IPC-A-600 Class 2/3, and IPC-A-600 Class 2/3.
PCBONLINE has long-term cooperation with China's top 3 mold and enclosure factories for the jigs and enclosures used in medical PCB assembly.
PCBONLINE has a global supply network and a component warehouse to ensure a stable and fast component supply for medical PCB assembly. Besides, it takes part in co-procurement with other EMS factories for components.
When your medical PCB project goes to the bulky production stage, PCBONLINE will refund you the fees for R&D, prototypes/samples, and functional testing. To get a quote, please contact info@pcbonline.com.
Conclusion
To conclude, the high quality of PCB ensures that medical devices will work efficiently and safely in critical healthcare environments. The process of developing a medical PCB involves choosing the right materials, type, and manufacturer that follows strict compliance with standards. Precision is essential for making medical devices reliable and trustworthy. To get one-stop medical PCB manufacturing, work with the turnkey advanced PCB manufacturer PCBONLINE.
PCB fabrication at PCBONLINE.pdf




